커맨드(Command) 패턴
06 May 2016 | 디자인패턴커맨드(Command) 패턴을 살펴겠습니다. 나중에 추가로 포스팅하겠지만, 먼저 다른 패턴들과 간단히 비교하면 다음과 같습니다.
- 스테이트(State) 패턴 : 상태 그 자체를 클래스화해서 사용
- 스트래터지(Strategy) 패턴 : 알고리즘 자체를 클래스화해서 사용
- 컴포지트(Composite) 패턴 : 각 객체들을 동일시화해서 사용
- 커맨드(Command) 패턴 : 명령 그 자체를 클래스화해서 사용하는 패턴
커맨드 패턴의 UML은 다음과 같습니다.
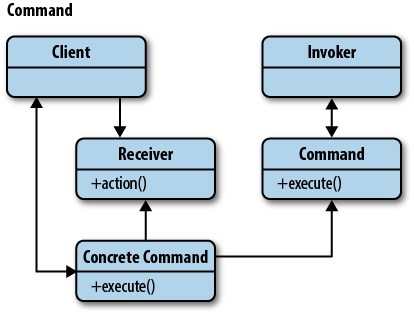
예제 코드
커맨드 패턴의 예제는 다음과 같습니다.
public interface Command {
public void execute();
}
이와 같은 인터페이스를 하나 구현하고, 각 명령을 구현하는 클래스들은 이 인터페이스를 구현(상속)하면 됩니다. 예를 들면 다음과 같습니다.
public class DrawCommand implements Command {
protected Drawable mDrawable;
private Point mPosition;
public DrawCommand(Drawable drawable, Point position) {
mDrawable = drawable;
mPosition = position;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
mDrawable.draw(mPosition.x, mPosition.y);
}
}
다음과 같이 Macro 형태의 Command도 만들 수 있습니다. Command들의 리스트를 이용하면 되는데, Stack, Queue, List 등 어떤 리스트든 성격에 따라 자유롭게 사용해도 됩니다. (여기서는 Undo, Redo 기능처럼 보이게 하기 위해 Stack을 사용했습니다.)
public class MacroHandler implements Command {
private Stack<Command> mCommandStack = new Stack<Command>();
@Override
public void execute() {
Iterator<Command> it = mCommandStack.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
((Command) it.next()).execute();
}
}
public boolean append(Command cmd) {
// 만약 자기 자신이 추가(append)되었을 경우 execute()에서
// 무한 루프로 빠질 가능성이 있기 때문에 미리 확인함
if(cmd != this) {
mCommandStack.push(cmd);
return true;
}
return false;
}
public void undo() {
if(mCommandStack.empty() == false) {
mCommandStack.pop();
}
}
public void clear() {
mCommandStack.clear();
}
}
